Deadlift is among the best compound exercises to strengthen the body, gain weight, and become an athlete. It will work on several muscle groups, such as hamstrings, glutes, back, and core, as well as enhance posture, endurance, and metabolism. This is regardless of whether you are a beginner or an experienced lifter, knowing how to deadlift is known to help gain strength, fat loss, testosterone levels and overall physique. The deadlift can be safely mastered by any person with constant training and sufficient rest, and tremendous progress can be achieved over time.
- What Is a Deadlift?
- Benefits of Deadlifts
- How to Properly Deadlift
- Muscles Worked by the Deadlift
- Deadlift Variations
- How Much Should You Deadlift?
- What should be the Number of Reps and Sets?
- What is your Deadlifting Frequency?
- Recovery and Safety
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Deadlifts vs Squats
- Deadlift and Hormonal Advantages
- In What Way and When to Add Deadlifts to Your Routine
- Final Thoughts
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Can beginners deadlift safely?
- 2. Do deadlifts burn belly fat?
- 3. What is the frequency of deadlifts per week?
- 4. Do deadlifts cause muscle growth and size?
What Is a Deadlift?
The deadlift is a compound weightlifting exercise whereby one lifts up a loaded barbell from the ground to the hip area and then brings it down again under control. It is a primary powerlifting lift (along with bench press and squat) and is thought to be the purest way of measuring overall body strength.
An effective lift needs strength, coordination and balance. It also utilises several large muscle groups, such as glutes, hamstrings, quadriceps, lower back, upper back, forearms, and core. It makes it a favourite exercise because it involves such a large number of muscles at the same time; it is referred to as the king of all exercises.
Deadlifting is beneficial in strengthening the posture, increasing grip strength, metabolism, and hormonal growth responsiveness. It is among the superior exercises that are used to develop strength, power, and resilience throughout the body.
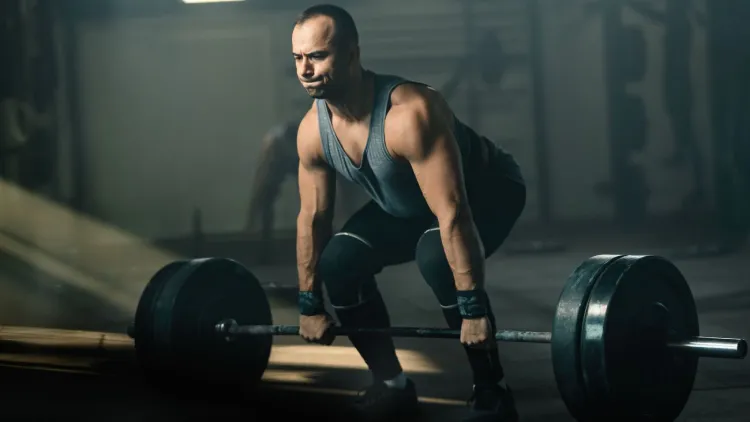
Benefits of Deadlifts
Deadlift has a lot of physical and psychological benefits:
- Full-body strength: Deadlift trains more than one set of muscles, therefore enhancing general strength and coordination.
- Growth of mass: Deadlifting done on a regular basis builds lean muscle in the legs, back, and core.
- Improved athletic performance: Glutes and hamstrings are stronger to enhance sprinting, jumping, and overall athletic performance.
- Better posture: The strengthening of the posterior chain decreases scoliosis and low back pain.
- Increased testosterone and growth hormone: Compound exercises such as the deadlift boost the production of natural hormones, which help grow the muscles as well as burn fat.
- Fat burning: Due to the high intensity of this compound form of movement, the lift increases metabolism and burns belly fat in the long run.
The deadlift is a good starting point when it comes to overall development of the body, be it to build muscle, develop fitness or advance athletic performance.
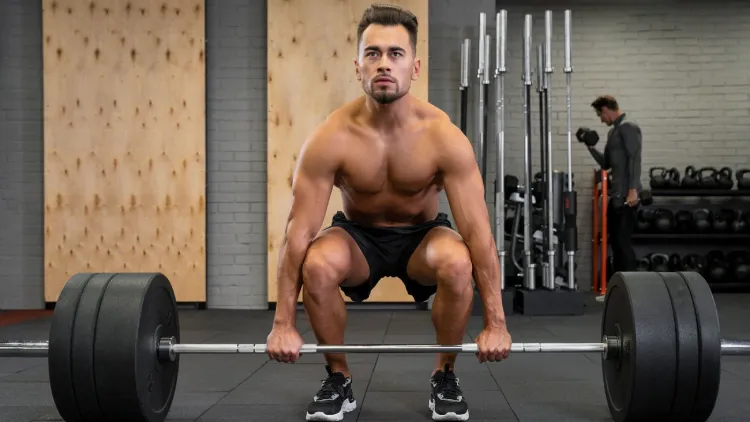
How to Properly Deadlift
As a beginner, one should know how to do it correctly to prevent harm and benefit the most. The following is how to do a traditional barbell deadlift:
- Position: Stand with your feet placed shoulder-width apart with the barbell placed in the middle of your feet.
- Grip: Squat, bending at the hips and knees, hold the bar by either a double overhand grip or mixed grip.
- Back position: Strauss your back, chest lifted, and shoulders slightly ahead of the bar.
- Lift: Push yourself off using the heels, straighten the hips and knees at the same time and pick up the bar till you rise to a standing position.
- Lockout: Your ass should be tightened at the top without straining backwards.
- Lowering: Revert the movement gradually, with control, and return the bar to the floor.
Newcomers are advised to work with low weights and then master the technique before increasing the weight. With time, the strength and confidence will be developed through regular practice.
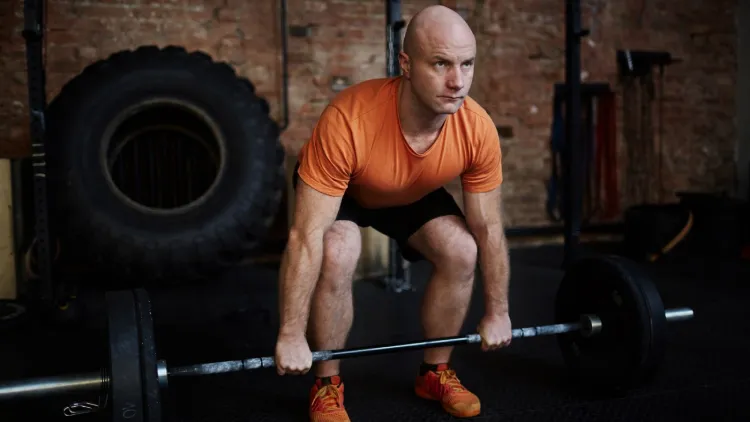

Muscles Worked by the Deadlift
The deadlift is a complex exercise which involves almost all the major muscles, and these are:
- Hamstrings and glutes: These are the muscles that make the lift and assist in the extension of the hips.
- Quadriceps: This helps at the first stage of raising the bar on the ground.
- Erector spinae (lower back): This is what helps the spine to be straight and straight.
- Trapezius and lats: Assist in posture and aid in the lift.
- Core and abs: Hold the torso and do not allow the back to round.
- Forearms and grip: Improve hand and forearm strength.
In a nutshell, lifts not only increase muscle mass but also increase the strength of both the upper and lower bodies.
Deadlift Variations
The deadlift has a variety of variations that are focused on various muscles and alternative levels of experience:
- Sumo Deadlift: This exercise involves a wide position with the aim of eliminating stress on the lower back and focusing on the hips and quads.
- Romanian Deadlift: It is more hamstring and glute-based, and the knees remain slightly bent.
- Trap Bar Deadlift: A hexagonal bar is used and thus enables a more upright torso, which is suited to beginners.
- Deficit Deadlift: This improves the range of movement, with the strength being developed on the floor.
- Dumbbell Deadlift: A Huge fitness option at home and to enhance grip stability.
The pros and cons of each variation are unique, and one of the necessary things needed to avoid plateaus and develop balanced strength is a rotation of variations.
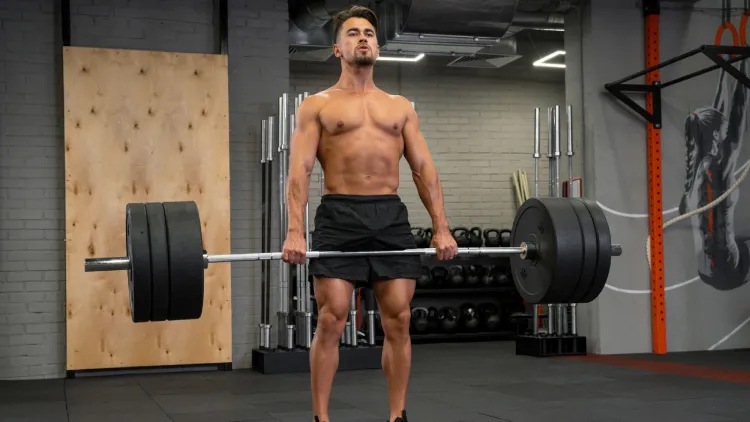
How Much Should You Deadlift?
A good starting point is 80-120kg of lifting (depending on the experience and the stage of training) for a 70 kg man. A 100 kg deadlift is normally impressive among most beginners, though the advanced lifters target 1.5 to 2 times their bodyweight.
One of the typical measurements of strength athletes is a 2x bodyweight lift. Professional powerlifters can lift much more than this – the world record is over 500kg (1,102 lbs), including the well-known lift by Hafthor Bjornsson.
Novices must be gradual in their advancement and not too much in the numbers. Good form and consistency are more than ego lifting.

What should be the Number of Reps and Sets?
To gain strength, do sets of 3-5 reps with heavy weights 3-5 times. In muscle building (hypertrophy), 3-4 sets of 6-10 reps of moderate weight are to be taken. Novices may be assigned 8-10 reps in 2-3 sets as a form of learning and endurance building.
One of the most common strength programs, the 5/3/1 method, relies on progressive overload, meaning that the weight is added gradually after every four-week cycle in an attempt to gain strength long-term.
What is your Deadlifting Frequency?
Novice deadlifters ought to lift once or twice a week so that they can rest sufficiently. Since it is a demanding activity, muscles and the nervous system require rest and become stronger.
Powerlifters or advanced lifters can train lifts 23 times per week, alternating between heavy and lighter technique training.
Recovery and Safety
When it is done properly, deadlifting is safe. Nevertheless, strain may occur because of poor technique or excessive training, particularly lower back. Always warm up, keep the spine straight and do not jerk the bar off the ground.
Depending on the intensity, people require recovery time depending on the intensity although most people require 48-72 hours before they hit their next heavy session. Stretching, sleep, and food are all helpful in quickening the recovery.
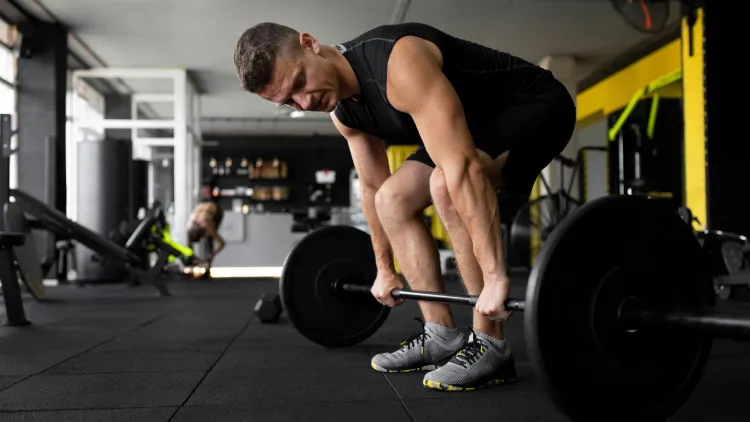

Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Rounding the back: May be severely injurious. Keep your spine neutral.
- Bar excessively distant from the shins: Lowers leverage and puts more stress on the back.
- Pulling the bar: Pull in a smooth motion so that you can control it.
- Overtraining: Have rest days to avoid fatigue and injury.
- Bad shoes: Do not use running shoes; use flat, stable shoes or lifting shoes because these have better grip and balance.
Deadlifts vs Squats
Both deadlift and squat are fundamental compound lifts, which are useful for different muscles. The lift puts more emphasis on the posterior chain, glutes, hamstrings, and back, whereas the squat is concentrated on the quadriceps and the general leg power.
The deadlift is more challenging to many lifters due to the fact that it originates at a dead angle on the floor and thus requires greater power of the posterior chain. The two exercises are complementary and need to be included in a balanced strength program.
Deadlift and Hormonal Advantages
Deadlifting has also been found to elevate the levels of testosterone and growth hormone naturally. These hormones lead to muscle building, strength and fat burning off- particularly in the midsection. This is part of the hormonal action that makes the lift a great workout for an individual wishing to gain muscle mass and lose belly fat at the same time.
In What Way and When to Add Deadlifts to Your Routine
The majority of lifters like doing lifts either on leg day or back day, depending on the focus. It is best to do them at the beginning of your workout when you have the most energy and get the maximum strength and performance.
Deadlifts may be accompanied by such exercises as squats, lunges, and core training to make a complete lower-body workout. Novices can use light weights or dumbbells before using barbells.

Final Thoughts
Deadlift is not only a strength workout but also a total body workout that works the muscles, increases posture, athleticism, and fat burning. Be it your intention to add muscle mass, move heavier or simply become fitter, learning how to do lifts will enable you to accomplish it sooner.
Through the correct method, slow building up, and enough rest, anyone can justifiably squat heavier, feel stronger and be assured or certain of their physical strength. The lift is a traditional representation of strength, discipline and will, which has stayed the same since the simple practitioners have moved up to elite powerlifters.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can beginners deadlift safely?
The only answer is yes, deadlifting, being a beginner exercise, is safe provided that it is done with the right form and at moderate weights. One should begin with a light load, work on technique, and warm up before the heavy weights. Correct posture, maintaining neutrality of the spine, and gradual development will minimise the chances of injury and ensure the strength increase will be maintained in the long term.
2. Do deadlifts burn belly fat?
Absolutely. Deadlifts are a total body compound exercise that has high calorie burning and raises metabolism. They are effective in decreasing total body fat, including belly fat, when paired with a balanced diet and regular workouts, as they use large muscle groups and increase testosterone levels.
3. What is the frequency of deadlifts per week?
Novices are advised to do lifts once or twice a week in order to give the muscles and the nervous system time to rest well. The more advanced lifters may train two or three times per week, with the first session being heavy lifting and the second and third sessions being technique-oriented light workouts.
4. Do deadlifts cause muscle growth and size?
Yes, deadlifts are among the best practices that would develop the mass of muscle and the absolute size of the body. They exercise large muscle groups such as the glutes, hamstrings, back and the core. Frequent deadlifting also enhances the production of testosterone and growth hormone, which contribute to muscle building and gaining strength.







