The rowing machine is one of the most efficient total body workout devices that enables the training of strength, cardiovascular fitness, burning of body fat and performing a movement that does not produce a strain on the joints. It has the potential for body fat reduction and endurance with correct technique and constant training, muscle strengthkneees protection, and body restructuring in the long run. This paper concentrates on the exercise of a rowing machine; its mechanism, the muscles involved, the duration required, the anticipated outcome, the most common mistakes made, and its comparison with other forms of exercise based on the principles of movement, physiology, and training.
- What Is a Rowing Machine Workout?
- Muscles involved in Rowing Machine Exercise
- Rowing Machine Exercise Benefits
- Correct Rowing Machine Technique
- Popular Rowing Machine Workouts Failures
- Beginner Rowing Machine Workout
- Medium Rowing Machine exercises.
- High-Level Rowing Machine Exercise
- Rowing Machine Fat Loss Exercise
- Strength Endurance Exercise on the Rowing Machine
- Breathing in Rowing Exercise
- Core Stability and Rowing Machine Exercise.
- Rowing Exercise Warm-Up and Cool-Down
- Frequency of Rowing Machine Workout
- Should everyone do Rowing Machine Exercise?
- Other Exercise Effects related to Rowing
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Is a Rowing Machine Workout?
A rowing machine is an activity that imitates a biomechanical motion found in pulling a boat through water. The process of rowing, as opposed to other single-plane activities like walking or cycling, comprises a coordinated pull, core stabilisation, and upper-body pull, unlike other exercises. This renders the use of the rowing machine a complex exercise equipment that engages more than one muscle group at a given time.
The rowing machine is powered by resistance using air, water, magnetic or hydraulic-powered but the pattern of motion is identical from the exercise point of view. A stroke involves force production, control, and rhythm, and this renders rowing effective in the exercise of aerobic and anaerobic exercise.
Fitness-wise wise the rowing machine can be used as:
- A cardiovascular endurance measuring device.
- A strength-endurance trainer.
- A fat-burning exercise
- A conditioning procedure of low impact.
Because it involves working with a large number of systems simultaneously, rowing is usually regarded as one of the most comprehensive exercises that can be provided.
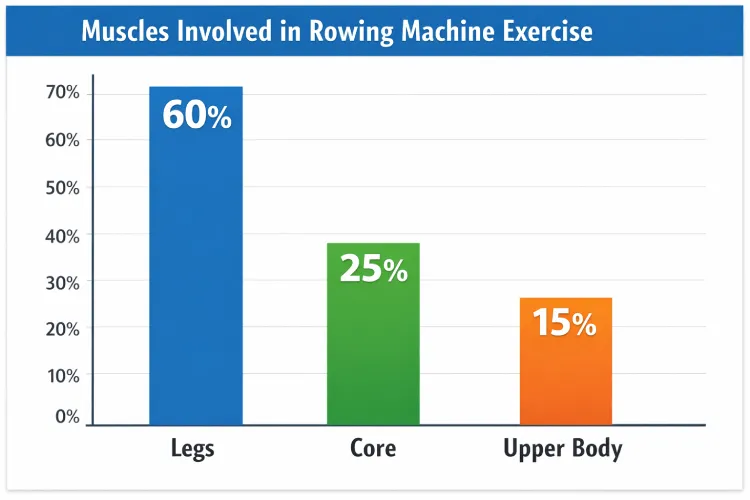
Muscles involved in Rowing Machine Exercise
The number of muscles it uses during one stroke is one of the distinguishing benefits of using the rowing machine as an exercise method. There are hardly exercises that provide the distribution of workload throughout the body.
Lower Body Muscles
It involves around 60 per cent of the power in rowing produced by the legs.
- During the drive, the quadriceps straighten the knees.
- Hamstrings help in the extension of the hips.
- This is stabilised or provided with force by the glute muscles.
- The ankle is stable in the calves.
Rowing is a good substitute for high-impact exercises of the lower extremities, particularly for people who are sensitive to the knees.
Core Muscles
The core plays the central role of a power pivot between the arms and the legs.
- The rectus abdominis secures the control of the trunk.
- The obliques stabilise the rotation.
- Erector spinae aid in the alignment of the spine.
Regular rowing improves the core without flexion of the spine repeatedly, which is a healthy attribute in the long term for the back.
Upper Body Muscles
It is involved in the pulling movement of the rowing machine:
- Latissimus dorsi
- Trapezius
- Rhomboids
- Biceps
- Forearms
- Rear deltoids
Rowing engages the majority of the muscles, but it does not emphasise as much on the chest muscles as well as vertical pressing muscles; it may be necessary to include some extra exercises in case of achieve the required upper body balance.
Rowing Machine Exercise Benefits
Full-Body Conditioning
The rowing machine is a machine that almost works out the whole body in a single motion. This renders exercises efficient in time and metabolically strenuous.
Effective Fat Burning
Since rowing combination of large muscles, it enhances the burning of fats and calories. When used along with suitable intensity and rest, regular rowing can decrease fat stored, such as abdominal fat, with time.
Low-Impact on Joints
Rowing is done in a sitting position and with controlled movement, which leads to a reduction of the stress on the joints. This can be implemented with individuals who experience knee pain, stiff joints, or individuals who are recovering from the effects of impact injuries.
Cardiovascular and Metabolic Health.
Rowing will help make the heart stronger and enhance blood flow, increase sensitivity to insulin, and well metabolic efficiency. These long-term health effects are useful, such as control of blood sugar.
Improved Body Shape
As a result of regular training on a rowing machine, most individuals achieve a better body tone in the legs, back, shoulders and core with the body composition significantly changing.
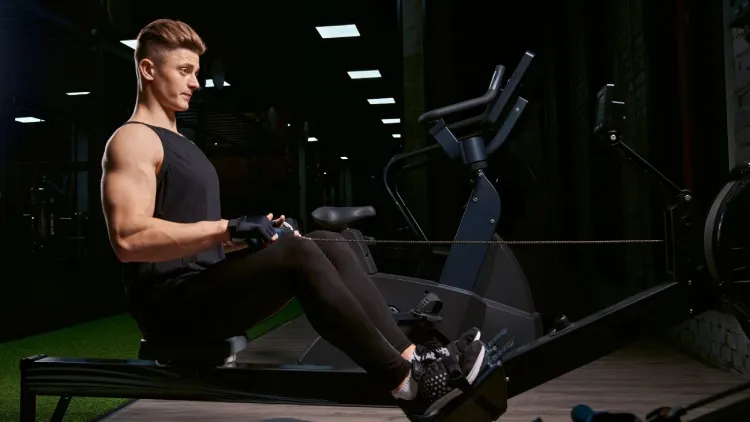

Correct Rowing Machine Technique
Correct technique provides precaution, productivity and best outcomes.
1. The Catch Position
- Knees bent
- Shins nearly vertical
- Arms straight
- Torso, slight forward bending.
- Core engaged
The posture puts the body in a good driving posture.
2. The Drive Phase
- Push through the heels
- Extend the legs first
- Engage the core
- Pull the handle towards the lower ribs.
Legs ought to be considered sources of power as opposed to arms.
3. The Finish Position
- Legs fully extended
- Handle close to the torso
- Elbows pulled back
- Lying or slightly tilted back torso.
- This step is the end of the stroke.
4. The Recovery Phase
- Arms extend forward
- Torso leans forward
- Knees bend last
- Slow and gradual recovery enhances endurance and technique.
Popular Rowing Machine Workouts Failures
One of the major causes which makes people not see results is bad rowing.
- Making a premature tug with the arms.
- Maintain a neutral spine throughout the stroke
- Keep a controlled, upright posture at the finish
- Use resistance that matches your strength and technique
- Focus on a smooth and steady recovery phase
Correct technique improves efficiency, reduces strain, and helps prevent injuries.
Beginner Rowing Machine Workout
Rookies are supposed to focus on skill and regularity rather than intensity.
A simple beginner structure:
- 5 minutes easy rowing
- 10–15 minutes steady pace
- 3–5 minutes cool-down
Still, brief sessions aid in developing coordination, stamina and self-confidence on the rowing machine.
Medium Rowing Machine exercises.
The intermediate rowers enjoy organised variability of intensity.
Example:
- 3 minutes moderate rowing
- 1 minute easy pace
- Repeat 6–8 rounds
This type enhances cardiopulmonary ventilation and calorie burning, and avoids boredom.
High-Level Rowing Machine Exercise
Intensity manipulation is applied in advanced training.
High-intensity rowing:
- Short, powerful strokes
- Higher resistance
- Interval-based sessions
The method improves power generation, heart efficiency and after-exercise calorie expenditure.
Rowing Machine Fat Loss Exercise
Rowing helps in losing fat through enhancing the daily use of energy and mitigation of metropolitan wellness. Although no exercise will burn fat in any particular part of the body, regular rowing will burn fat in the whole body that including fat in the abdomen.
Long, steady, and short-term training are all effective in losing fat as long as they are properly coupled with recovery.
Strength Endurance Exercise on the Rowing Machine
The lower speeds of strokes and with regulated power will contribute to the development of muscular endurance with less strain on the joints. Through consistent, controlled movement, the legs, central area and upper extremity become collaborative over a length of time that enhances endurance and body density. This ensures that the rowing machine is suitable for athletes who want to maintain their performance during intense workouts, as well as the elderly who require a low-impact exercise method for building up muscles. With continuous use over time, there is increased muscle strength and cardiovascular output, resulting in the ability to work longer without exhaustion and a reduction in the risk of injury.
Breathing in Rowing Exercise
- Breathing rhythm influences the performance.
- Inhale during recovery
- Exhale during the drive
- This shape leads to oxygen delivery and consistency of stroke.
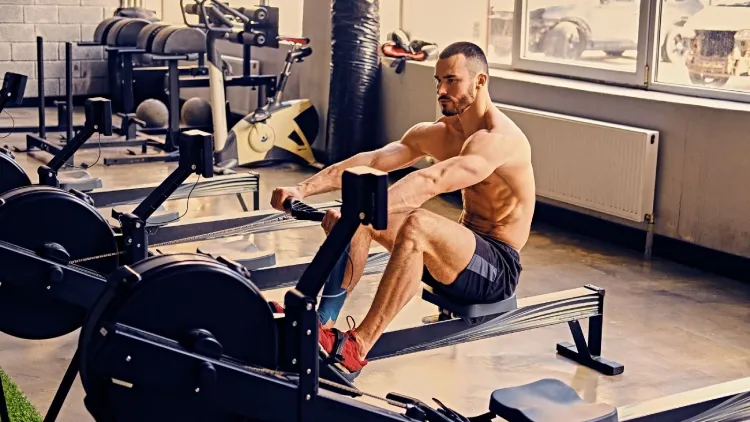

Core Stability and Rowing Machine Exercise.
Working out at the rowing machine enhances the core by giving consistent, controlled exercise instead of brief and intermittent contractions. The core muscles remain active throughout every stroke to make the spine straight and pass the strength of the legs to the upper body. This prolonged stimulation enhances core endurance, which is more operative as compared to short core training.
Since rowing involves sitting with the neutral spine and a coordinated movement, it assists one in strengthening proper posture and spine position. In the long term, it will result in a more upright stance, a higher level of trunk control, and a lesser load of the lower back during both exercise and everyday life. Proper technique rowing fosters core strength effectively and safely, with feelings of not subjecting stress on the spine.
Rowing Exercise Warm-Up and Cool-Down
Warm-up and cool-down will assist the body to enter and leave the exercise in the rowing machine safely and efficiently. These phases aid in joint health and enhance performance, as well as decrease muscle stiffness following training.
Warm-Up
Start with gentle paddling in a slow manner that increases the heart rate slowly and warms the muscles. The resistance should be minimal, and the strokes need a smooth and controlled nature. When the body becomes relaxed, the length of strokes and the strength of legs should be increased without changing posture. A short warming up of five minutes is a preparation of legs, core and upper body to more vigorous rowing.
Cool-Down
Once the workout is complete, lower the intensity and bring down the rowing speed and pace for several minutes. This enables the breathing and pulse rate to become normal. Continue with light stretching of legs, back, shoulders and arms in order to ease stiffness and aid recovery. An adequate post-workout enables a person to avoid tiredness and to be prepared for the second rowing session.
Frequency of Rowing Machine Workout
The optimum frequency of exercise on the rowing machine is based on the training experience, recovery capacity and fitness objectives. Although the process of rowing is a low-impact exercise, it imposes a lot of stress on the muscles, the cardiovascular system, as well as the nervous system. The required time between sessions ensures that the body adapts, recuperates and develops better performance with the passage of time. The role of consistency, as opposed to high volume, is the most significant in long-term outcomes.
Beginners: 2–3 Sessions per Week
A rowing machine workout should be done progressively for beginners. Doing two to three sessions a week enables the body to get used to the movement pattern without much fatigue and soreness. The main purposes at this level will be the correct technique, the development of a minimal level of endurance, and the strengthening of stabilising muscles.
First-time sessions must be of moderate intensity and duration, which should be between 15 and 25 minutes. The days that are in rest between the sessions assist in the deterrence of overuse injuries, and in particular in the lower back, shoulders and forearms. It is a method that allows for maintaining a gradual pace and reducing the chances of burnout or discomfort.
Intermediate: 3-4 Sessions a Week
As soon as the technique is trained and the base endurance is reached, it is possible to conduct exercise on a rowing machine three to four times a week. In the middle tier, the organism can withstand the stresses of training more, and a combination of aerobic rowing and anaerobic training can be made.
Depending on the intensity, the length of the session can be extended to 20-40 minutes. The necessary recovery is necessary, and rowing continues to put a strain on the muscle and cardiovascular systems. The alternation of more intense sessions and light recovery rows is effective in performance continuity and preventing plateaus.
Advanced: 4–6 Sessions per Week
With proper management of the recovery, advanced exercisers will be able to exercise on the rowing machine four times a week. Exercises at this level can be of differing intensity, length and the rate of the strokes, aimed to achieve endurance, power and conditioning.
Usually, besides the high-intensity intervals or longer endurance rows are low-intensity recovery sessions in advanced rowers. Although lifting regulates muscle balance and joint health also recommends regular rowing to boost efficiency and aerobic power; one rest day or light day per week is enough to keep the body and muscles in balance.
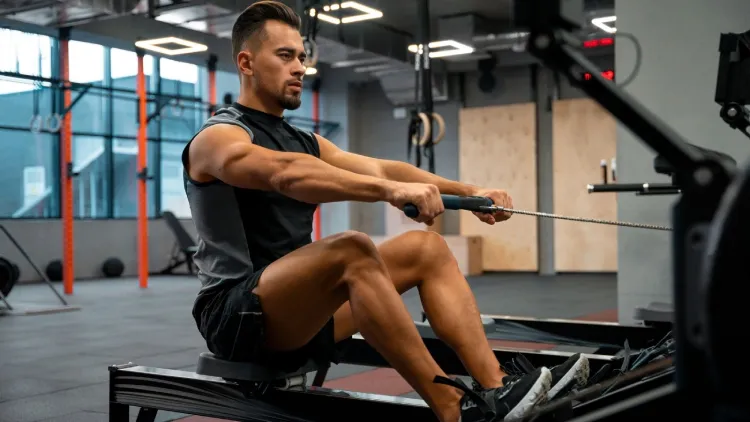

Should everyone do Rowing Machine Exercise?
The exercise of a rowing machine is appropriate to the bulk of the population since it is a low-impact exercise, which can be adjusted and well-controlled. Those with low resistance may take short sessions as beginners in order to develop endurance and correct technique without straining the joints. The reason why seniors tend to enjoy rowing is due to its gentle nature of moving in a sitting position that does not strain the knees and hips but does give them strength, balance, and cardiovascular benefits.
The rowing machine is used by athletes in conditioning and endurance training as well as in recovery because it does not impose repetitive impact on the whole body. Rowing can be a safe practice for those who experience joint pain or those who have been injured in the past, provided that they maintain the proper form and exercise intensity is moderate. The trick lies in emphasising delicate movements and slow development.
In spite of the fact that rowing is an ideal activity in the majority of fitness levels, individuals with severe back or shoulder problems are supposed to be cautious and consult a professional beforehand. The rowing machine is one of the most flexible and integrated forms of exercise that can be used when used properly.
Other Exercise Effects related to Rowing
Fitness can be greatly enhanced in just 30 days through regular exercising with a rowing machine, further stamina, better muscle tone and enhanced cardiovascular efficiency. It takes changes in body composition in most people within 3-6 weeks.
Rowing would be better than walking, cycling and the use of a treadmill because it engages the entire body. Although walking is less vigorous, rowing is more caloric per minute. Rowing entails greater activation of the upper and core with compared to cycling. In comparison with treadmill running, rowing has a reduced impact on joints and equally cardiovascular benefits.
Rowing is also joint-friendly when done properly, hence it is appropriate for people who complain of knee pain. Rowing is not like jumping or sprinting, as it does not subject the body to repeated loading of impacts.
Rowing is excellent for full-body strength and endurance, and while it primarily targets the back, legs, and core, complementing it with chest or vertical-pushing exercises can create a perfectly balanced workout.
Rowing may be done at high intensity and burn a lot of calories; however, it is unwise to push oneself to high calorie rates without condition, without resulting in fatigue or bad form. These outcomes may be achieved through gradual training and not extremes.
Rowing helps balance blood sugar levels and maintain good health systems, and, therefore, it is helpful to people with insulin resistance. Rowing can be used during pregnancy, although it should be done only in the early stages, with the recommendation of a medical professional and in a low-intensity and correct posture.

Conclusion
A rowing machine is one of the most comprehensive exercise equipment. It strengthens, increases stamina, cardiovascular fitness, and muscles and is low-impact and versatile. Rowing machine exercise benefits the body when performed with correct form and frequency, and can redefine the body and help it reach target fitness without being unduly stressed by its many joints.
Knowing how to row, how much time to spend on training, and how to organise workouts will make the rowing machine not only a cardio device, but also an effective basis of total body exercise.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Does exercise on a rowing machine reduce belly fat?
Yes, rowing utilises huge muscle groups, and this enables more calories to be burnt and which helps get rid of the fat around the belly.
2. What is the duration required to realise the results on a rowing machine?
Regular workouts of 20 – 40 minutes, 3-5 times a week, generally demonstrate enhanced stamina and muscle tone in 3-4 weeks.
3. Will rowing be better for the knees than other cardio exercises?
Yes, rowing is low impact, which causes less stress on joints, hips and ankles, and is therefore perfect for individuals with joint problems.
4. What is the comparison of rowing with treadmills or stationary bikes?
Rowing trains the body as a whole, which includes cardiovascular and strength. It is also less impactful than treadmills; it works more muscles compared to bikes.







