Mass gainer is something that can help in muscle building, however, at the expense of properly planned, progressive, and intense physical workouts. Adequate compound lifts, effective training division, and planned recovery, as well as steady improvements, are what define whether calories are represented as fatty tissue or lean body mass. The use should be safe, at the correct time, with realistic expectations and knowing the limits of your body is important. This is your ultimate training guide, which includes how to train, how to be strategic with gaining weight, who must not use a mass gainer, and how to be the most effective with exercise science.
- The Reason to Exercise with a Mass Gainer
- Top Activities to Add to a Mass Gainer Diet
- Best Weekly Exercise Split to Gain Mass
- Progressive Overload: The Secret of Improvement
- Rep Ranges for Maximum Mass
- Recovery and Rest Training Principles
- Most Exercise errors in using a Mass Gainer
- Intense Training to gain more mass rapidly
- Side Effects, Who Should Avoid It, and Safety
- Realistic Expectations of Gaining Weight
- Principles of Eating to Support Training
- Learning Fat and Muscle Distribution
- Final Thoughts
- Frequently Asked Questions
The Reason to Exercise with a Mass Gainer
A mass gainer is made to help gain muscle weight and build up, yet the workout defines the calibre of such gain. Excess calories without resistance training can only result in more fat in the body. Opposed to unstructured training in strength production, however, mass gainer assists in the recovery, performance, and lean muscle production.
Exercise produces microscopic tears in the muscles. Through the healing process, these fibres are mended and made stronger and heavier. This process is assisted by a caloric excess. That is why the intensity of training is of much more importance than an increase in calories.
The question many novices pose is whether a mass gainer would be good to exercise with. This will require varying training plans. A mass gainer can also be used to address the needs of people with limited appetite to consume adequate amounts of food to sustain intense training. But, unless there are compound lifts, as well as progressive overload, there will be only limited results.
Hormone production is also affected by exercise. Squats and deadlifts initiate the release of testosterone and growth hormone because of heavy lifting. Such hormonal reactions increase the potential of building muscles, and the body can effectively utilise nutrients.
In case you are underweight, that is, by 10kg or more, structural resistance training together with proper calorie intake becomes even more important. A very low level of weight may impact power, energy, and health. The safest and most appropriate way is gradual and controlled weight gain by way of exercise and nutrition.
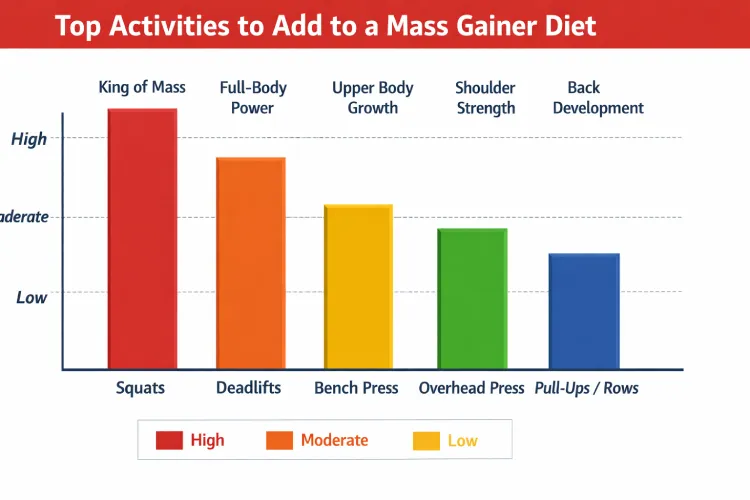
Top Activities to Add to a Mass Gainer Diet
When including a mass gainer in your regimen, it is important to pay attention to such exercises that encourage the greatest muscle involvement. The basis of your program should be made up of compound movements.
1. Squats (King of Mass Building)
Squats utilise the greatest number of muscles in the body, and therefore, it is probably one of the best exercises for size and strength.
Benefits:
- Develops quads, hamstrings and buttocks.
- Improves core stability
- Improves the strength of the lower body.
- Supports hormonal response
Squats, which are heavy, provide a powerful anabolic atmosphere. For people who want to gain 7 kg or more, it is advisable to make lower-body compound exercises a priority to stimulate the muscles more.
Workout Tip:
- 4–5 sets of 6–10 reps
- Add on weight every week.
- Rest 90–120 seconds
Another effect of training in the legs is the way that your body stores excess calories. Intensive training of major muscle groups leads to the movement of nutrients into muscle repair during the training rather than into fat storage.
2. Deadlifts (Full-Body Power Exercise)
Deadlifts engage several muscles at the same time: the back, glutes, hamstrings, and core.
Why Deadlifts Matter:
- Build overall thickness
- Increase grip strength
- Strengthen the posterior chain
- Enhance the overall coordination.
The deadlifts particularly work well when one is aiming at gaining weight in a systematic way. Rather than focusing on whether the improvement of 10 kg over two weeks is possible, it is more reasonable to pay attention to the gradual enhancement with the help of heavy and controlled exercises.
Routine Suggestion:
- 3–5 sets
- 5–8 reps
Do at least once a week with the best.
3. Bench Press (Upper Body Growth)
The bench press has been one of the most dependable mass builders in the upper body.
Targets:
When working on hypertrophy, the main ranges of rep to use are moderate and strict. Assemble Swedish squats that are low, mid, and fatigue.
Suppose that you have a monthly weight-gain goal of 7 kg, and you have exercised your upper body using progressive overload training and exercises, combined with standard calorie consumption. The combination offers the best opportunity to see any type of improvement.
4. Overhead Press (Shoulder Development)
Thick shoulders develop a good physique. Movements which involve overhead pressing enhance the strength and stability of the upper body.
Recommended Structure:
- 3–4 sets
- 8–10 reps
- Maintain controlled tempo
5. Pull-Ups and Rows (Back Thickness)
Symmetrical development depends on the back development. The density and posture of the upper body are increased through pull-ups and rowing movements.
Include:
Train back muscles twice a week to stimulate growth.

Best Weekly Exercise Split to Gain Mass
The first alternative is a 5-Day Muscle-Building Split
- Day 1 – Chest & Triceps
- Day 2 – Back & Biceps
- Day 3 – Legs
- Day 4 – Shoulders
- Day 5 – Heavy Compound Full Body
Option 2: Push-Pull-Legs
- Push, Shoulders, triceps– Chest.
- Pull – Back, biceps
- Legs – Lower body
- Repeat twice weekly.
The frequency of the training is more important than the random increase in calories. Every three hours might be the solution to the calorie intake of some people, but ultimately, it is exercise that will ensure one gains muscle.
Progressive Overload: The Secret of Improvement
Progressive overload refers to progressive building up of training demands. In its absence, the muscles die off and shut down.
Methods include:
- Adding weight
- Increasing reps
- Improving technique
- Slowing tempo
Claimed weight gain. Minute weight gain claims, including 1kg in a day or 7kg in 7 days, are impractical and, in most cases, are water retention and not muscle growth.
Rep Ranges for Maximum Mass
Rep ranges are very important in effectively building muscle. When combined, various repetition ranges create different stimuli in the body, and when used tactfully, they create maximum growth.
5–8 reps: Strength Focus
This reduced spectrum of reps focuses on more weight lifting. The two aspects of neural efficiency and raw strength are the main benefits of training in this zone. When the load is heavier, a lot of muscle fibres are recruited, and this is the recruitment of the fast-twitch fibers which can be grown well. The rest durations typically have more time (90120 seconds or more) to provide time for recreational time between sessions. Training within this variation assists you in raising heavier weights at a later stage of hypertrophy-oriented sets.
8 -12 reps: Hypertrophy (Muscle Growth)
This has been largely regarded as the most productive range of the size of the muscles. It establishes a middle ground between the mechanical stress in load (heavy enough) and metabolic stress (muscle fatigue and pump). The rep range 8-12 is a time span sufficient to force growth and provide enough of a challenge to the muscle at the same time. The duration of a rest is between 60 and 90 seconds. This is the range you should work at in most exercises directed at producing size.
12-15 reps: Muscular Endurance and Control
Increased reps and moderate weight have the benefit of enhancing muscular endurance and ensuring that more blood reaches the muscles. This range is not so strength-oriented and can be used to augment muscle conditioning and potentially assist in improved form, stability, and mind-muscle connection. It can be employed frequently in the use of accessory movements or finishing exercises.
To achieve high-maximal-mass one should use the majority of working sets in the range of 8-12, supplemented by some heavy-load (5-8) and high-voltage (12-15) training. This balance prevents the development of strength, size, and endurance one-sidedly.

Recovery and Rest Training Principles
It is during recovery that the increases in muscle actually take place. Exercise causes muscle tension, which is relieved through rest to enable such fibres to repair and become stronger. Without rejuvenation, any additional calories will likely be stored as fat rather than being utilised to build lean muscle.
Give a minimum of 48 hours of rest before training the same muscle group, and have at least one or two days of rest per week. Light exercise, like walking or stretching, will aid in the circulation of blood and does not overtax the muscles.
Rest is a significant factor in sleep. The growth hormone is released during deep sleep, and it assists in repairing muscle tissue. Get 7- 9 hours of good sleep per night to aid in strength gains and normal body composition.
Hydration is also essential. Water assists in absorbing nutrients into muscles, and it also generally boosts performance. Always drink during the day, particularly around exercise.
To achieve proper monitoring of the progress, weigh yourself every day at the same time. Weight on waking up after going to the restroom has the best consistency. Pay attention to trends of the week and not the day.
Most Exercise errors in using a Mass Gainer
- Training intensity in overeating.
- Ignoring form
- Skipping leg workouts
- Excess cardio
A mass gainer is not magic. Discipline is the most important thing in training.
Intense Training to gain more mass rapidly
After establishing a good base using compound exercises and progressive overload exercises, the next step is to use more advanced training exercises capable of defeating plateaus and triggering further muscle development. These modes cause greater intensity, better recruitment of muscle fibers and an enhanced resultant training stress. They can bring great improvements when used appropriately.
Drop Sets
The drop sets are the exercises performed to the edge of failure, and the weight is immediately decreased, and the exercise is carried on without rest. This is a method that strains the muscles to the limits of their fatigue.
For example:
- Complete 10 bench presses using a difficult weight.
- Reduce the weight by 20–30%
- Repeat as many repetitions as possible.
The drop sets are more fatiguing in the muscle and are capable of metabolic stress, both of which are causes of hypertrophy. They particularly work best at the end of a workout when you would like to have the full exhaustion of a certain group of muscles.
Supersets
Supersets are targeted at two exercises done one after the other. These may involve the adjacent muscle groups (compound supersets) or antagonistic muscle groups (antagonist supersets).
Examples:
- Immediately after biceps curls, perform triceps extensions.
- Push-ups and bench press in that order.
- Squats followed by lunges
Supersets maximise the intensity of the workouts and minimise the duration of the training. They also enhance muscle endurance and improve the pump to aid the growth of muscle as more blood flows to the muscle.
Rest-Pause Training
Rest-pause training is an alternative form of training that enables you to use heavier weights but with more total reps after a brief element of rest accompanying one set.
How it works:
- Do a heavy set to what amounts to almost failure (e.g. 6 reps)
- Rest for 10–15 seconds
- Perform 2–3 more reps
- Rest once more for a moment and repeat.
This system extends the amount of training and does not reduce the intensity. It also puts a strain on strength and endurance, in that it is effective when it comes to breaking a strength plateau.
Time-Under-Tension Training
Time-under-tension (TUT) is based on taking control of time to increase the repetition to the length of time, making the muscle hold or stay active. Rather than lifting, you have either control of the lifting (concentric) or lowering (eccentric) phases.
Example tempo:
- 3 seconds lowering the weight
- 1 second pause
- 2 seconds lifting
The muscles gain more stress and consequently better growth stimulus by increasing the number of reps. TUT is also good at enhancing form and the mind-muscle relationship.

Side Effects, Who Should Avoid It, and Safety
A mass gainer can be considered safe by a regular trainer with good health conditions. Nevertheless, when it is used too much, it may lead to stomach fluid discomfort, bloating, or undesirable weight gain.
An increase in protein intake can cause symptoms like nausea, dehydration, or stomach strain if one takes it in excessive quantities. The normal kidneys are able to process protein efficiently, and people with kidney disease ought to stay away of protein high supplements unless under doctor supervision.
Individuals who are intolerant to dairy products or who have metabolic conditions or difficulty regulating blood sugar need to consult the professionals prior to use.
Doctors recommend the use of weight gain supplement but only under medical advice, where the patients are underweight.
Feeding on the appropriate use of a mass gainer, there is no scientific evidence that suggests its strong impact on reproductive health.
Realistic Expectations of Gaining Weight
Becoming 2 kg lighter over 10 days can be a result of being in a glycogen storage and water retention. Advanced muscle gain begins at 0.25 -0.5kg/week.
Rather than drastic goals, such as 10 kg in two weeks, devote attention to methodical training, sufficient protein consumption (approximately 30 grams per meal with such products as chicken, eggs, lentils, Greek yoghurt), and calorie excess.
Whole foods are not that insignificant. Healthy fats, nuts, lean meat, dairy, and rice, along with potatoes, are in favour of steady growth.
Principles of Eating to Support Training
The use of the protein within 30 minutes of the training and the equal balance of the macronutrients is commonly known as the 30-30-30 strategy of post-training consumption. The 3-3-3 eating concept emphasises the idea of having balanced meals during the day.
The eating culture in Japan focuses on the concept of moderation and not eating to the full. The golden rule of eating aids conscious eating.
The increase in weight should be more of quality, rather than quantity.
Learning Fat and Muscle Distribution
The distribution of fat and muscle is different in each individual. Genetics and hormones mainly determine the source of fat storage within the body. There are those who will accumulate fat around the belly, and other people can accumulate fat in the thighs, hips or even in the face.
At the onset of fat loss, it is not on any particular part, and it is not due to training on the specific part. Fat is minimised by the body on the whole, and fat areas which tend to reduce earlier are based on the natural body build. The reason is that some individuals may put on facial fat in the initial stages, while others notice a difference in their arms or legs initially, before the stomach.
Muscle gain, as with differentiation, is a different matter. Training stimulus is directly linked to the growth of muscles. The lower part of your body will grow if you regularly do squats and lunges to train your legs. When you put emphasis on bench presses, rows and shoulder presses, your upper body will become bigger and stronger. Muscle development is like effort, intensity, and progressive overload, unlike fat loss, which follows the genetic trends.
This is because spot reduction is also a myth. Infinite belly exercises will help in tightening the muscles of your abdomen, yet will not directly eliminate belly fat. Resistance training with total body involvement, coupled with consistent effort, will result in proportional fat loss and muscle development in the long term.
Simply put, there is no way to stop the location of the fat, but you can stop the location of muscle by properly training those muscles and regularly so.

Final Thoughts
A mass gainer is beneficial to exercise performance when taken in moderation. It is not a shortcut but an addition to rigorous training. Emphasis should be kept on heavy compound lifts, progressive overload, sufficient rest and realistic expectations.
Moderate, gradual advancement will never be as effective as drastic approaches. The development of muscle needs patience, organization and organisation. Exercise intensity becomes sustainable when the calorie intake is equal to the exercise intensity.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is it necessary to use a mass gainer to build muscle?
The growth of the muscles does not require a mass gainer. It is merely an easy means of adding calories for people who face quite a challenge in meeting the adequate number of calories through whole food items. Growth of muscles is majorly reliant on progression resistive training, recoil and constant excess of calories. When you can get your nutritional requirements through normal meals, then you might not require a supplement.
2. What is the most effective rate of muscle building?
It takes time to gain healthy muscles. Novices can accumulate about 0.25-0.5kg in a week when they are put under optimal training and recovery conditions. Within a few days, it is often possible to gain quite rapid weight not as a result of muscle growth but instead because of water retention or an increase in glycogen stores. Training and nutrition consistency bring long-term outcomes.
3. When is it advisable to take a mass gainer?
Post-workout is traditionally the most efficient period of time because the muscles after the training are already prepared to receive nutrients. Other people also take it between meals in order to achieve their daily calorie needs. Recovery is aided by timing, although maximum daily consumption and training are more important than timing.
4. What are the side effects of using a mass gainer?
A mass gainer would be relatively safe among healthy individuals when taken sensibly. But when consumed excessively, it can cause bloating, stomach upsets or unwanted weight gain. Individuals who have kidney disorders, metabolic diseases or are intolerant of dairy products should discuss taking high-calorie supplements with a healthcare professional.







