The most important muscle for shoulder strength, shape, and mobility is the deltoid. The three heads need to be trained: front, middle, and rear to develop balance, avoid injuries, and perform effectively. This manual includes exercises on specific muscles, multi-joint movements, suggestions on rapid development, and preventive measures against overtraining, including the reasons behind weakness, the presence of nerves, and indications of muscle problems.
- Anatomy of the Deltoid
- Parts Exercises Deltoids Warm-Up
- Best Exercises
- Complex Reduction of the Shoulder
- Guidelines to Maximal Deltoid Development
- Sample Workout Routine
- Weaknesses are commonly caused by the following.
- Summary: Knowledge of Deltoid Health and Pain
- Advantages of Developing the Deltoids
- Professional Training Tips
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Anatomy of the Deltoid
This is an oblique-shaped muscle that gives the rounded shape of the shoulder, also known as the shoulder cap. Lifting, rotating, and stabilizing the arm depend on it. Its key motions are shoulder abduction (lifting the arm sideways), flexion (lifting the arm forward), extension (moving the arm backwards), and rotation.
The deltoid is three-headed, and each of the heads performs a certain role:
- Anterior (Front): Located on the anterior part of the shoulder, it participates in pushing movements such as overhead presses and front raises.
- Lateral (Middle): It is located on the outer part and plays the biggest part in the shoulder’s widest dimension, and works when doing a lateral raise.
- Posterior (Rear): They are located at the back of the shoulder and hold the shoulder together in pulling movements, and maintain good posture.
Learning these heads is relevant in structuring a deltoid-based exercise. The three will all make sure the body is balanced in terms of strength, the muscles of the shoulder will be working in the right direction, and the chances of getting an injury will be minimal, not to mention that performance and the image will be better.
Parts Exercises Deltoids Warm-Up
Appropriate deltoid and shoulder joint warm-ups ensure that the body works hard to lift the set weights. Failure to do this exposes the strains and overuse injuries.
- Arm Circles: Rotate your arms forward and backwards or 1-2 minutes. This activates the shoulder joint and involves all the heads of the deltoid.
- Shoulder Shrugs: Strain your shoulders upward towards the ears and then drop in maximum time. Repeat ten to fifteen timestoo be able to move the upper trapezius and rear delts.
- Resistance Band Pull-Aparts: Take a band at the height of the shoulders and pull the band at a slow pace. This incorporates the posterior deltoid and stabilizing muscles.
Scapular Push-Ups: Moving the shoulder blades towards and away from each other in a nursery fashion, activating the stabilizing muscles protecting the deltoid during the scapula.
Warmed up not only avoids injury but also pre-heats the deltoid to grow and develop strength.
Best Exercises
Hitting all three heads of the deltoid will give equal strength andan attractive appearance. The following is a detailed analysis of exercises:
1. Front Deltoid Exercises
- Overhead Press: Overhead pressing of weights using dumbbells or a barbell is a movement that involves the activity of the anterior deltoid, triceps, and upper chest. Keep the abdominal muscles strong to ensure that you support the lower back.
- Front Raises: Lift the dumbbells or a plate weighing one of your shoulders using front raises to the level or just above your shoulders, where you should hold a short pause before you continue.
- Arnold Press: Turn your palms during the press to use all the anterior deltoid to give a special contraction that makes growth.
Such exercises are necessary to give strength and definition to the front deltoids that prevail in most pushing motions.
2. Lateral Deltoid Exercises
- Lateral Raises: This is the quickest way of developing middle delts. Keep the elbows slightly bent and do not swing as much as possible.
- Row out of the upright: Week, a dumbbell or a barbell entirely up to the chin. Attract attention to some movement in control to avoid the shoulder impingement and concentrate on the lateral delts.
- Cable Lateral Rises: The cable ones will guarantee that the deltoid is under constant tension during the movement, which is optimal in hypertrophy.
Middle delts are the ones that help most with the width of the shoulders. Focusing on such exercises enhances the box and general strength.
3. Rear Deltoid Exercises
- Reverse Flys: Bend a little forward at the hips and grab out dumbbells to the side, and squeeze the shoulder blades together.
- Face Pulls: Draw with the help of a cable machine, a rope fixation, and pull it towards your face. This not only develops the back delts but also promotes the health ofthe rotator cuffs.
- Bent-Over Lateral Raise: Do this on slow, that is controlled motions to ensure that the posterior is utilized to the fullest.
Rear delts are used and help to enhance posture, stability of the shoulders, and avoid injuries in case of press-pull exercises.
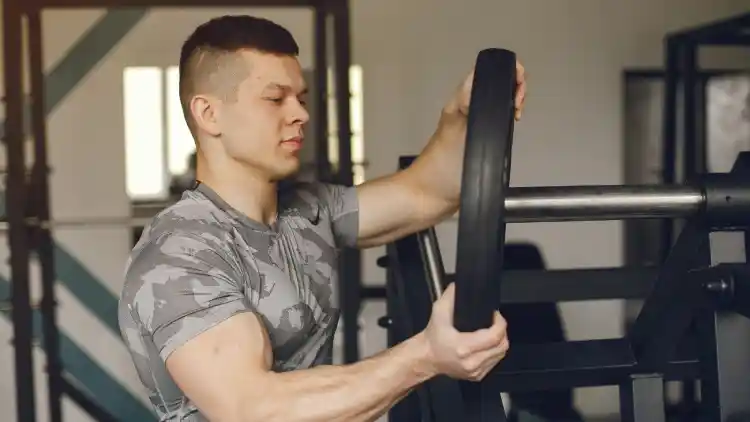

Complex Reduction of the Shoulder
Compound lifts engage several heads and other muscles, making them stronger, more powerful, and coordinating the muscles.
- Military Press: This is a barbell press overhead, which is designed to be a front or middle delt Madnessexercises but incorporates triceps and upper chest.
- Push Press: Push press is a combination of the leg drive and shoulder pressing that enables the heavier loads to promote growth in all deltoid heads.
- Dumbbell Shoulder Press: This can be done in a natural motion, causes minimal strain, and hits the muscles.
- Clean and Press: This is a dynamic lift, but involves deltoid working on several planes and enhances power, strength, and shoulder mobility.
The combination of compound movements with isolation exercises is the best way to develop your shoulder muscles to the maximum.
Guidelines to Maximal Deltoid Development
- Mind-Muscle Connection: To achieve hypertrophy, the deltoid is better contracted on every rep.
- Progressive Overload: You can add weight or reps gradually and repeatedly challenge the deltoid.
- Correct Form: Do not move forward, swing, or jerk; this will avoid injury and give an optimum movement through the deltoid.
- Deloits are relatively small muscles and must rest. Overuse injuries may be caused by training on a daily basis. Targets are 48 72 intensive hours.
- Balance Training: Front, lateral, and rear delts should be included to prevent any imbalance and lack of strength.
To develop them within a short time, exercises must be done regularly, in good shape, and with good mixes.
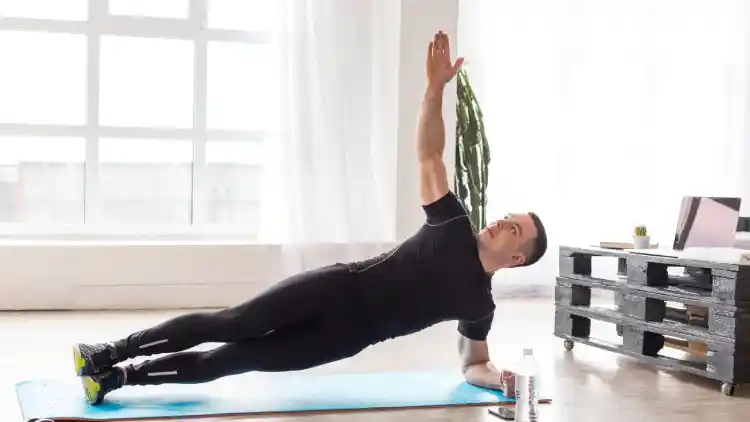

Sample Workout Routine
Advocate to intermediate plan that includes each of the deltoid heads:
- Overhead Dumbbell Press: 4 sets and 10 reps.
- Lateral Raises: 3 sets × 12 reps
- Front Raises: 3 sets × 12 reps
- Reverse Flys: 3 sets × 15 reps
- Face Pulls: 3 sets × 12 reps
Off-peak this once or twice every week. Add warm-up and cool-down so that it becomes less sore and will not cause injury.
Weaknesses are commonly caused by the following.
The poor deltoid muscles can be due to several factors:
- Wrong Form of Training: Activation and growth are decreased because of poor lifting.
- Rotator Cuff Problems: Rotator cuffs are weak or torn, which hamper the functioning of the deltoid.
- Nerve Damage: axillary nerve dominates the deltoid; it might be damaged as a result of which the person may experience weakness or atrophy.
- Oversight: When training frequency is excessive (lack of rest), the strength gains are decreased.
- Nutritional Deficiency: A lack of protein, vitamins,s or minerals may compromise the growth of muscle.
The cause of these can be identified at an early stage so that corrective action is taken to normalize deltoid strength.

Summary: Knowledge of Deltoid Health and Pain
The is either overused, traumatised, or hit by the nerve:
- Pain: This is painful or soreness in the shoulder, which occurs mostly during pulling or turning.
- Deficiency: An inability to perform its duties effectively because of the destruction of nerves or because of muscle degeneration.
- Weakness: The inability to raise objects, tiredness during pressing actions, or the loss of the shoulder shape.
- Nerve Involvement: The axillary nerve is the one that controls the work; this may be traumatized or compressed.
- Muscle Disease: There are some muscle diseases or systemic disorders that begin with the proximal muscles.
The first sign of a weak condition or pain is the initial step to minimizing the harm. Underlying causes can be diagnosed with the help of blood tests and vitamin assessments.
Advantages of Developing the Deltoids
By building up good deltoids, there are several benefits:
- Enhanced Shoulder Stability: Cushions joints in your day-to-day activities and heavy lifting exercises.
- Improved Beauty: Finely-built delts make shoulders wider and more prominent.
- Functional Strength: This is necessary to push, pull, and overhead.
- Injury Prevention: Prevention of rotator cuff strains and impingement of the shoulder.
- Posture Support: A strong rear delts is effective in keeping the back in a straight position and prevents strain on the back.
Good deltoids are the source of performance and attractiveness, and hence one should give much attention to deltoids in case he or she is concerned about upper body training.
Professional Training Tips
- 3-3-3 Rule in the Gym: Have three sets of three exercises using all the heads of the deltoid muscle to help them grow equally.
- Stress Reduction: Swelling, continual soreness, or poor performance are all symptoms of overtraining,g but at an initial stage.
- Choice of Exercises: Compound lifts, along with isolation exercises that strike all three hheadss provide comprehensive growth.
- Recovery and Nutrition: Proteins are sufficient with a proper amount of vitamins (B12, D) as well as minerals (magnesium).
Use the following tips to gain it quickly, lessen the chances of injury, and be able to live with your shoulders.

Conclusion
This is one of the muscles that are essential in measuring strength, beauty, and fitness. It gives the same concentration on the anterior, lateral,l and posterior head with the combination of compound exercise and isolation exercises so as to achieve balanced development. Training: Do not terrorize yourself, focus on recovery, and keep good form to get the most out of training.
The deltoid muscle not only weakens your appearance but also contributes to better performance by strengthening, protecting joints, and minimizing the possibility of injury. Neglecting proper exercise can leave you with arms that look and feel a lot softer than you want, but with practice and intelligent efforts, you will be able to develop strong, shaped, and prominent shoulders to serve both daily needs and advanced body lifting.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the deltoid, and why does America want to know?
The deltoid is a triangular muscle on the shoulder that raises, turns, and gives the arm some stability. It contributes significantly to the functionality and the shoulder aesthetics. Deltoid strengthening enhances the upper body strength and posture in exercises such as the presses, raises, and draws.
2. Would I be training my deltoids odaily
Deltoids are not suggested to be trained daily. Similar to any other muscle, the deltoids require rest, particularly after uncommon loading. The effect of overtraining is soreness, fatigue, or even an injury. Preferably, they should be trained 2-3 times a week and should rest during the intervals.
3. Which are the exercises that stimulate all three heads of the deltoid?
All three heads of the deltoid are used in such compound moves as the overhead, dumbbell shoulder press, and push press. Combining them with isolation exercises, such as lateral raises, front raises, and reversefliess, is the means of providing the balanced development of the shoulders.
4. What are the indicators of weak deltoids or overtraining?
Weak deltoids can result in problems lifting objects, a lack of shoulder stability, or an unbalanced appearance. The problem of overtraining is characterized by constant soreness, swelling, poor performance, and fatigue. Adequate relaxation, sleep,p and moderate exercises keep the deltoid muscles healthy.







