Inverted rows are among the best exercises that are used to build the back, arm strength and core strength using bodyweight. They train the lats, upper back, biceps, forearms, and muscles that maintain stability and also enable the beginners and advanced trainees to train at a level of their convenience. Inverted rows are ideal in callisthenics programs, clients’ workout plans, and exercises at home and aid in muscle building, good posture, and reducing body fat, as long as they are combined with the appropriate training volume. Their flexibility can be defined as a cornerstone movement towards long-term strength building.
- What Are Inverted Rows?
- The Working muscles in Inverted Rows
- Benefits of Inverted Rows
- Learning to do the perfect inverted rows
- Inverted Row Variations
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Inverted Rows vs Pull-Ups
- Inverted Rows: How to Include Inverted Rows in Your Workout
- The Inverted Rows and Callisthenics Training
- Construction of a Huge Back With Inverted Rows
- Substitution of Machines and Free Weights
- Arm Development and Strength of Grip
- Successful Row Types and Training Charges
- Fast Processing and Cardiovascular Improvement
- Final Thoughts
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Inverted Rows?
Inverted rowing involves a pulling exercise in which the entire body is held by a hanging bar, rings, or some hard surface with the heels planted on the floor. The motion entails drawing the chest to the bar and having a straight and rigid body posture. Directional movement.e Unlike vertical pull-ups, inverted rows are horizontal instead of vertical and thus simpler to scale and less joint-zapping.
This exercise is now common icallisthenicscs, functional fitness, and as a strength training method since athletes can be able to train to develop pull strength without necessarily being suspended with their full body mass. Inverted rows also place a lot of emphasis on scapular control and are very beneficial to the health and posture of the shoulder.
Since the weight can be decreased or increased merely by switching the position of the feet or bar height, inverted rows can be used by almost every level of experience. First timers need to begin with bent knee positions, beginners with higher feet or beginners with tempo plus pauses.

The Working muscles in Inverted Rows
They are a complex movement as they utilize many muscles at once and, therefore, inverted rows, as they have a high rate of training.
Primary Muscles
- The latissimus dorsi width of the back and the force of pulling.
- Scapular retraction: Rhomboids and middle trapezius.
- Elbow flexion:n Biceps brachii.
- Shoulder balance Rear deltoids.
The secondary and Stabilizing Muscles
- Endurance Forearms and grip muscles, which have a significant role in pulling.
- Erector spine assist in the upkeep of the spine position.
- The core muscles consist of the transverse abdominis and the obliques.
- Stabilisers of the lower body are the glutes and hamstrings.
Since the inverted races need a straight posture of the body, it acts as a whole-body movement and not merely a back movement.
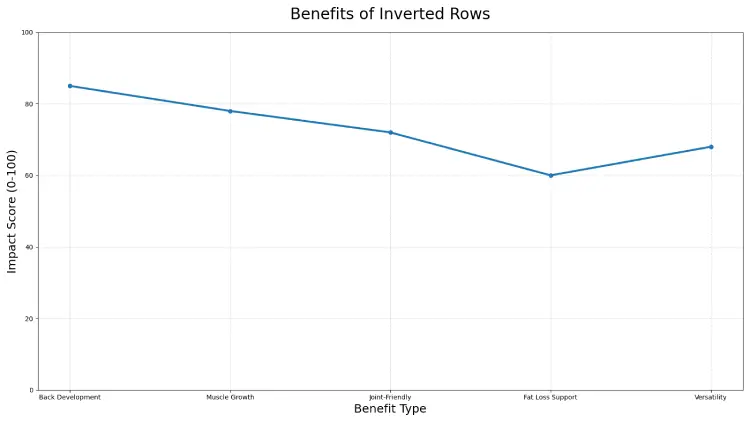
Benefits of Inverted Rows
Inverted rewards have much more than just aesthetic advantages.
Balanced Back Development
The inverted rows enable a natural scapular movement as opposed to machines, which fix movement paths. This encourages a stronger, healthier, well-rounded muscular growth of the shoulders.
Muscle Growth Potential
Inverted rows, although a bodyweight exercise, can develop very significant body mass with gradual overloading. Hypertrophy is also brought about by increased leverage, reduced tempo, pauses and manipulation of volume.
Joint-Friendly Pulling
Vertical pulls are not done by many lifters because of discomfort in the elbow or shoulder. Inverted rows are associated with stress-free joints and high muscular activity.
Fat Loss Support
Even though inverted rows burn calories and promote lean muscle mass as well as metabolic demand when done with adequate volume, no single exercise specifically combats belly fat.
Versatility
They may be done in the gym, parks or at home with minimum equipment.
Learning to do the perfect inverted rows
IGC enhances greater muscle activation and minimises injury by performing the exercise correctly.
Aim at placing a bar at the waist.
- Lie in the back and embrace the bar a little bigger than the shoulders.
- Lengthen legs and strengthen core and butt.
- Maintain a straight position of the body with the head and heels.
- Pull the chest in the direction of the bar and start with the elbows.
- My top squeeze in the shoulders.
Lower under control
The optimal height of the bar is dependent on the level of strength. Taller bars make the work harder, whereas shorter bars make the work easier. The breathing needs to be constant with exhalation during the pull.
Inverted Row Variations
Bent-Knee Inverted Rows
No equipment Bent-knee inverted rows are the best choice at the beginning, as the body warms up, or for high-rep work. Bending the knees causes the body to be more upright, and therefore the resistance is lower,d and the body is easier to control. It is this difference that contributes to the building of appropriate pulling mechanics and scapular motion, and then the harder types.
Feet-Elevated Inverted Rows
Inverted races with feet raised make the task impressively harder as they shift a larger portion of the bodyweight to the pull. Raising the feet on a bench or box places a more horizontal position of the body with increased results of the upper back, lats and arms being activated. This is the variation that is normally applied in strength and muscle building.
Wide-Grip Inverted Rows
The wider grip puts more focus on the upper back, especially the rhomboids, trapezius and back deltoids. This difference can be applied to enhance the back thickness and shoulder balance. The control is also essential because with too wide a width, the range of motion may decline if the control is not done well.
Underhand Grip Inverted rows
Underhand or supinated grip involves more of the biceps, yet the back muscles are the same focus. This difference is efficientforo those that want to gain both arm and back strength. It also permits a little more of a range of movement of the elbow.
Single-Leg Inverted Rows
Inverted rows will involve a balance and stability test by lifting one foot off the ground. The difference enhances core involvement and makes the body counter-rotate to provide favourable total control and coordination when pulling.
Ring Inverted Rows
Ring inverted rows cause instability that involves a larger degree of involvement by people to stabilise the shoulders, arms and the core using more muscles. This variation moves the rings independently and naturally in the wrist and shoulder position, and this, together with the positioning, makes this movement rather difficult and joint-friendly when done under control.

Common Mistakes to Avoid
Reven, considering mere movements, they can become ineffective when done in the wrong way.
- Allowing the hips to sag or pike
- Momentum replacements are pulled off by momentum.
- Failure to scapularly retort an entirety.
- Cutting the range of motion
- Over-wringing of the neck onto the bar.
When these problems are rectified, the muscle involvement and permanent improvements would be significantly enhanced.
Inverted Rows vs Pull-Ups
The two exercises are useful pulling exercises, although they have diverse uses.
Pull-ups focus on vertical pulling force and scapular dominance, whereas inverted rows focus on horizontal pulling as well as scapular action. Inverted rows are also used by many athletes as a stepping stone towards pull-ups, although they are also used to supplement the vertical pull to ensure full development of the back.
Other bodybuilders reduce the amount of pull-ups per joint load and recovery effort by substituting them with rows, where the load is more manageable. This has no impact on effectiveness- rowing movements continue to be the basis of back size.
Inverted Rows: How to Include Inverted Rows in Your Workout
Inverted splits are inverted in almost every training split.
- Strength Focus
- 4–6 reps
- Longer rest periods
- Weighted or high-jumped feet.
Hypertrophy Focus
- 8–12 reps
- Moderate tempo
- High time under tension
Endurance Focus
- 12–20 reps
- Short rest intervals
They go well together with push-ups, squats, hinges and core work.
The Inverted Rows and Callisthenics Training
Callisthenics is based on the control of bodyweight. The callisthenics programs include inverted rows as one of the large base exercises of the pulling exercises, the other two being the push-ups and squats. They aid the development of muscle-ups, front lever, and advanced pulling ability.
Numerous training ideologies are 80/20-driven, meaning that although a large amount of attention is given, a small number of compound actions can provide the highest outcomes. Inverted rings are in that high-payoff category.
Construction of a Huge Back With Inverted Rows
Inverted-Ps are capable of definitely developing a thick and muscular back when developed progressively. The key factors are:
- Progressive overload
- Sufficient weekly volume
- Full range of motion
- Consistent tension
They are aimed at hitting the same muscle groups as barbell, dumbbell, and cable rows, so they should be considered a valid alternative when the equipment is not available.

Substitution of Machines and Free Weights
Inverted row is a good alternative to rowing machines and free weights since it readily resembles the horizontal pulling motion, and one is also free to move around. This is because this liberty of movement promotes alignment of the natural joint and enhanced muscle coordination. Inverted rings may be used to conduct home training on a stable table, suspension straps, rings, or a fixed bar, meaning they are very versatile without any special equipment.
Despite the dumbbells and cables having accurate weight control, inverted rows have more emphasis on body control, stability and core involvement. This makes them particularly valuable in enhancing joint resilience and functional strength, whilst giving adequate resistance to muscle development when progressed under control.
Arm Development and Strength of Grip
The grip strength is significant in inverted rows and tends to increase rather quickly through training. Although the grip strength can not be a direct measure of the hormones, the stronger the grip, the higher the overall strength and neuromuscular efficiency.
Inverted legs also help to develop arm with intense use of the biceps. Although isolation, such as curls, is not useless, the overall muscle recruitment is provoked by the compound pulling exercises.
Successful Row Types and Training Charges
Rowing activities should be the most suitable exercises as far as they give the possibility of the full movement of the shoulder blade and constant muscle tension. The inverted rows accomplish this by encouraging the correct scapular control and pull control throughout the entire range of motion.
Simple training rules (e.g. adding total reps, lessening rest time, decreasing tempo to make it harder) can also be well-handled by them. These methods make inverted-rows easy to adjust to various levels of strength because they enable progression without the need to incorporate additional weight.
Fast Processing and Cardiovascular Improvement
Rowing exercises increase the heart rate as they involve several muscles which work simultaneously. Inverted rows elevate total training output and energy loss when undertaken in increased repetitions or in a circuit. Though they do not actually target fat loss in particular areas, they help in burning calories overall, which aids in burning body fat.
Inverted rows are also instrumental in the maintenance of lean muscle mass in times of fat loss. The importance of maintaining muscle is to sustain an efficient metabolism, and the pulling actions of the body, involving compounds exercise offers an effective stimulus without being overly stressful to the joints. The inverted rows are low impact and scalable, which can be applied so often to enhance conditioning, muscular endurance, and work capacity,y among other bodyweight motions.

Final Thoughts
One of the most effective, adaptable, and sustainable exercises is the inverted-row because it offers constant strength and growth of the muscles. They develop the back, arms and core and also strengthen the healthy movement patterns. Invested in callisthenics, gym, or home training, inverted reverses are one of the foundation exercises that will provide the same results as long as there is purpose and progress in training.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is there a replacement for the rowing machines with inverted rows?
Yes thehorizontal pulling action of rowing machines, inverted rows, has a strong ability of recreating this motion, but it was made more natural. They exercise the back, arms and core without requiring the locking of the body to a specific direction.
2. Is it possible to invert a row at home even when there is no equipment?
Inverted rings could be done at home with a firm table, suspension straps, rings or any stable bar that was placed at a suitable height.
3. Which is better between the inverted row and the dumbbell or cable row?
Dumbbell and cable rows can be loaded accurately, but the inverted rows enhance the coordination, core stability and joint control. They both work, based on training objectives.
4. Are inverted pads beneficial to the health of the joints?
Yes, inverted rows allow the free movement of the shoulders and the maintenance of controlled tension, which could help to increase the strength of the joints in case of their correct implementation.







