One of the best ways to strengthen the upper body, increase muscular endurance, engage the core, and become a more fit person is to learn how to do a pushup correctly and only use bodyweight as the training tool. Push-ups are an exercise that strengthens triceps, shoulders, core, as well as the stabilising muscles, so they can be done by both beginner and advanced trainees, teens, and adults alike. Gradual development of the form, correct breathing and correct variations is what enables anyone, whether he cannot do a single push-up or someone who is advanced in training, to gain strength and performance with proper training in the push-ups.
- What Is a Push-Up?
- Muscles Worked in a Push-Up
- How To Do a PushUp: Step-by-Step Directions
- Correct Push-up Form Checklist
- Breathing When doing Push-Ups
- Top Errors to Prevent in Push-Ups
- Push-ups Variations According to Fitness Level
- Push-Up Repetitions and Sets
- Push-Ups and Core Stability
- Push-Ups as a Bodyweight Training Exercise
- Master the Push-Up With Starting Zero Strength
- Push-Ups in Teens, Kids, and Age
- Push-Ups and Development of the Chest
- Push-Ups, Fat Loss and Body Composition
- Push-Ups during Military and Athletic Training
- Push-Ups and Ab Engagement
- Training Frequency for Beginners
- Symptoms of Overtraining with Push-Up
- Push-Ups in a Minimal Exercise Regimen
- Final Thoughts
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Is a Push-Up?
The push-up is a compound weightless movement that consists of lowering and lifting the body through bending and stretching the arms in a rigid and plank-like position. To know how to do a pushup, one has to begin by knowing that it is not only an arm exercise. It is a full-body motion that involves a combination of the upper body and central, hips, and legs.
The research aims to track the use of Push-ups in fitness testing, athletic conditioning, military training, and entry-level exercise programs since it is an effective test of upper-body strength and muscular control.
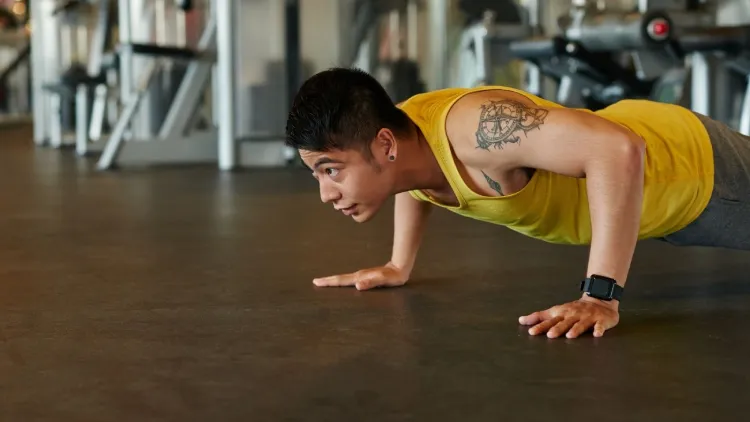

Muscles Worked in a Push-Up
The information about the muscles involved can assist in understanding why the necessity to learn how to do a pushup correctly is so important.
Primary muscles activated:
- Muscles of the chest (pectoralis minor and major)
- Triceps brachii
Front shoulders (anterior deltoids)
- Stabilising and secondary muscles:
- Abdominal muscles
Obliques
- Lower back muscles
- Glutes
- Back and serratus anterior.
Since push-ups involve a large number of muscles simultaneously, they enhance general strength and coordination instead of training a certain group of muscles.
How To Do a PushUp: Step-by-Step Directions
To learn proper technique of the pushup, one must pay attention to alignment, tension and movement in control.
1. Starting Position
- Hands should be on the floor, but no more than shoulder-wide.
- Fingers extend forward or even outward.
- Bend straight backwards with feet on the ground.
- Maintain straight posture, head, shoulders, hips and heels.
- Engage core and glutes.
2. Hand and Arm Placement
- Shoulders directly followed by wrists.
- Elbows were folded in, not thrust out.
- Fingers squeeze and squeeze the floor.
3. Lowering Phase
- Breathe in, bending motion on the elbows.
- Tilted down to the ground at the lower chest under control.
- Have a straight body posture.
- Keep neck neutral
4. Bottom Position
- The chest floats above the ground.
- Elbows are folded at an angle of 45-60.
- Core remains tight
5. Pushing Phase
- Breath out, pushing the floor.
- Keep legs straight with arms straight.
- Maintain full-body tension
6. Repetition Control
- From repetitions, they should be smooth and controlled.
- Using bouncing or collapsing at the bottom is to be avoided.
Correct Push-up Form Checklist
The learning of how to do a pushup efficiently is based on correct form.
- Strict body positioning at any given time.
- Tight core and glutes
- Controlled tempo
- Elbows tracking backwards
- Full range of motion
- Shoulder in a stable position.
Having good form makes the activation of the muscles harmonised and minimises the stress on the joints that are not necessary.
Breathing When doing Push-Ups
Breathing contributes significantly to performance and endurance. It could not be overlooked when it comes to learning how to do a push-up.
- Breathe in at the descending stage.
- Breathe out in the pushing period.
- Avoid holding your breath.
- Rapid repetitions should be accompanied by steady, rhythmic breathing.
Proper breathing enhances power production and postpones exhaustion.
Top Errors to Prevent in Push-Ups
Many people can improve their push-ups significantly by focusing on proper technique.
- Engage your core fully to keep your hips aligned and support your lower back.
- Maintain a straight hip line to maximise chest activation and full range of motion.
- Keep elbows slightly tucked to protect your shoulders and enhance pushing strength.
- Use a full range of motion to activate all muscles effectively.
- Hold a neutral neck position to stay stable and efficient throughout each repetition.
By paying attention to these details, anyone can progress faster and perform push-ups with greater strength, control, and confidence.
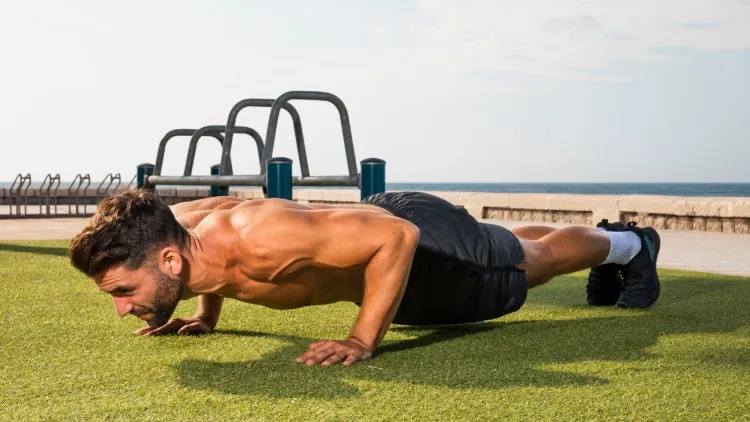

Push-ups Variations According to Fitness Level
When learning to perform a pushup, one must always make progressions, and it is critical when a person is beginning to learn to perform the exercise or regaining strength after an unintentional break.
Beginner Push-Up Variations
- Wall Push-Ups: Laid standing, pushed up against a wall. Perfectly suitable for extremely weak beginners.
- Incline Push-Ups: Placing hands on a bench, table or step. Lowers the resistance of the body weight.
- Knee Push-Ups: Bend on knees, keeping the upper body straight.
- Such differences can enable individuals who are unable to do a normal push-up to gain strength.
Middle Variations of Push-Up
- Standard Push-Ups: The movement with a complete use of bodyweight.
- Close-Grip Push-Ups: Bringing hands relatively closer to the underlined triceps.
- Tempo Push-Ups: The slow lowering stage enhances muscle control and strength.
Advanced Push-Up Variations
- Decline Push-Ups: Elevation of feet to raise the load on the chest and shoulders.
- Diamond Push-Ups: Heavy triceps emphasis.
- Archer Push-Ups: Weight one side to side to have unilateral strength.
- One-Arm Push-Up Progressions: Entails great strength, balance and control.
These differences have made the push-ups difficult, even with people who have been trained.
Push-Up Repetitions and Sets
Repetition plans rely on the goals and level of fitness and recovery capacity.
- Beginners: 2–3 sets of 5–10 reps
- General fitness: 3 sets of 10–20 reps
- Endurance focus: Increasing repetitions of moderate tempo.
- Strength: smaller amounts of reps with more difficult versions.
The 3 sets of push-ups with 10 reps are a good foundation of fitness, whereas the advanced programs have to evolve instead of being repetitive.
Push-Ups and Core Stability
One of the reasons why push-ups are tricky is the strain required on the core. In the instruction on how to perform a pushup, it is vital to engage the core.
- Abs brace the spine
- Glutes stabilise the hips
- Lower back remains neutral
Hence, the reason why push-ups are a good abdominal activation exercise, although they are not the normal ab exercise.
Push-Ups as a Bodyweight Training Exercise
Push-ups are part of the bodyweight training regimens applied in:
- Military conditioning
- Athletic development
- Youth fitness programs
- Home workouts
No equipment is needed, and they are easy to adjust to all the differences in strength levels, thus making them one of the most viable exercises.

Master the Push-Up With Starting Zero Strength
Most individuals find it difficult as they are unable to do a single repetition. Teaching the push-up technique will start with regression and time.
The successful steps in progression:
- Wall push-ups
- Incline push-ups
- Knee push-ups
- Negative (lowering-only) push-ups.
- Partial-range push-ups
Reducing aid progressively and gradually will enable strength to build in a safe and current manner.
Push-Ups in Teens, Kids, and Age
Push-ups are harmless weight-bearing exercises when started in the right form and under some supervision for children and teenagers. Exercises involving the use of body weight are generally adopted in the training of the youth as they apply controlled stress on muscles without any external load.
The performance according to age differs:
- Young people tend to develop faster because of are flexible.
- The strength development is based on consistency, technique, and recovery.
- Push-up skill is determined by the body weight, coordination and muscle development.
- Push-ups are often used as an indication of the general fitness in terms of age.
Push-Ups and Development of the Chest
The stimulation is effective with chest muscles with push-ups, especially with a full range of movement and progressive overload.
Nonetheless, the growth of the chest is dependent on:
- Progressive difficulty
- Adequate volume
- Recovery time
- Proper nutrition
It might be possible that only a high-repetition routine can increase endurance, but no longer than to maximise the size of the chest. More challenging forms of push-ups will be required for long-term muscle long term building.
Push-Ups, Fat Loss and Body Composition
Push-ups are effective in enhancing the body composition, but not in removing fat in a particular part of the body, such as the chest. The burning of fats occurs all over the body and not in a specific area. Eliminating fat on the chest requires the general body fat elimination, which is done through exercising and proper rest.
In regard to exercise, push-ups aid in burning fat as they maintain lean muscle mass. The importance of maintaining the muscle is that it ensures that there is physical activity of the body to be able to cope with normal training. Push-ups are also known to elevate the metabolic demand as they train as many as three muscles concurrently, such as the chest, shoulders, triceps, and core.
With an increase in upper-body strength, it is possible to increase the volume of push-up training and include more difficult variations. This added labour aids in the long-term gains in body makeup by combining muscle maintenance with constant calorie consumption.
Push-Ups during Military and Athletic Training
Push-ups are very popular in the training of military forces as well as sports activities due to the consideration of multiple factors simultaneously; they test the tests of endurance of the upper body and core stability, including the ability to control the movements. Rather than stressing the high repetitions that are reckless, these systems value high strictness in form, tempo and stabilisation in the quality of repetition. The pressure to be applied in a push-up should address certain requirements, such as proper body posture and maximum motion.
Push-ups are frequently applied in athletic training as warm-up exercises in order to work the chest, shoulders, triceps, and core before more serious work. They condition the upper body to be more explosive through training and endow a stable shoulder.
Push-ups are employed in endurance strength work, as well as they are repetitions of endurance exercises or performances with stopping clocks, which help the athletes to develop fatigue resistance. Also, they are effective as accessory exercises to aid in the strength of pressing and enhance muscular balance without placing so much strain on the joints.
Push-Ups and Ab Engagement
To avoid sagging or over-arching, push-ups must be done using constant abdominal tension. That is why push-ups enhance the endurance of the core in the long run.
Although they are not the direct abdominal exercises, push-ups:
- Enhance the profound deep muscles.
- Improve spinal stability
- Agreement of coordination throughout the body.
Training Frequency for Beginners
Training is as important as far as recovery is concerned in learning how to do a push-up. Muscles require some time to recuperate and acclimatise, and this is the reason why push-ups should not be performed too frequently at the beginning stage.
Training should be 24-4 days a week in most cases, when there is a beginner. This gives time to be strong and have the chest, shoulders, arms, and core to rest. The emphasis should be put on good form and small numbers that are repeated as opposed to large numbers.
The intermediate trainees can train frequently (3-5 days per week) with improved strength. The various variations of push-ups help to prevent overuse and achieve an equal development of the muscles.
Only under proper care of the load, advanced individuals can be allowed to do push-ups daily. It requires different levels of intensity and volume to prevent plateaus in the work of the joints and stress in the joints.
There is a way that they can work every day, but an excess of push-ups without rest or taking time off wastes away the gains and causes soreness and exhaustion.
Symptoms of Overtraining with Push-Up
Vertical Overtraining Because of the high volume of push-ups without rest, excessive volume of push-ups may result in:
- Decreased performance
- Persistent muscle soreness
- Joint discomfort
- Reduced motivation
- Training and rest balance make long-term progress guaranteed.
Push-Ups in a Minimal Exercise Regimen
Push-ups are also seen as being associated with other base motions:
- Squats
- Pulling movements
- Hinges
- Core holds
These movements constitute a comprehensive exercise system that does not need a lot of equipment.

Final Thoughts
Knowing how to do a pushup well will make it look like a mere motion instead of a strong, whole-body workout. When push-ups are done with the correct body position and increasing difficulty, the body muscles gain strength, stamina, coordination and core stability.
Whether you are a total beginner taking it starting from zero rather than the level of an athlete already practising their endurance, push-ups are one of the best and most versatile exercises that can be performed. The secrets to success in the long-term push-up training include stability, patience and focus on technique.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the duration of push-up strength?
It is normal to gain in push-up strength in a 2-4-week period with regular workouts. Novices can readily feel positive after engaging in correct form and taking on simpler variations and resting between sessions. It is all about consistency, technique, and gradual increases in difficulty to create progress.
2. Why is it harder to do more repetitions of push-ups?
The fatigue of the muscles and the demand in the core make the push-ups more difficult. The chest, shoulders, triceps and core grow fatigued, and thus it needs more effort to remain in the right position. This is healthy and shows that the muscles are being taxed well.
3. Do you need push-ups to have complete upper-body strength?
Push-ups are great as they build upper body push and core stability techniques, though likewise balancing training by pulling and lower-body practices. Push-ups are a good exercise that is best done in conjunction with the rest of the exercise program.
4. So what can I do in case I cannot do a complete push-up?
In case a full push-up cannot be carried out, then you can begin by doing wall push-ups, incline push-ups, and knee push-ups. These differences increase flexibility and develop power. The best process to improve in a safe way is to go gradually up to standard push-ups.







